Hvernig hundar sjá heiminn okkar og í hvaða litum. Myndadæmi
Efnisyfirlit
Hvaða liti sjá hundar best?
The stereotype that the world of the dog is a solid black and white movie was destroyed a long time ago. True, this was done without sensational disclosure of facts. So when an unusual article about canine perception appeared in the Daily Mail, some animal lovers were very impressed.
Photographs of a company that organized travel for people with pets prompted journalists to talk about the “vision of the world” by pets. In the photo, the travel agency showed how top English sights look like through the eyes of people and dogs. The difference was enormous, although veterinarians noted that in some ways the content creators were not entirely objective. Nevertheless, the marketing ploy worked: the company’s customer flow increased dramatically, and dog owners became even more interested in the perception of their own wards.
In reality, the advertisers did not make any scientific discoveries, but simply wrapped the well-known information in a spectacular “wrapper”. The fact that animals distinguish colors quite successfully, although the palette available to them is poorer than a human, is known to every dog owner who is at least minimally aware of the work of the pet’s senses. The reason for less colorful perception is the number of visual receptors located on the retina (cones). There are three types of people. Dogs have only two.
Þér til upplýsingar: if you rely on exact numbers, then a person has as many as 6 million visual receptors, a dog has 1,2 million.
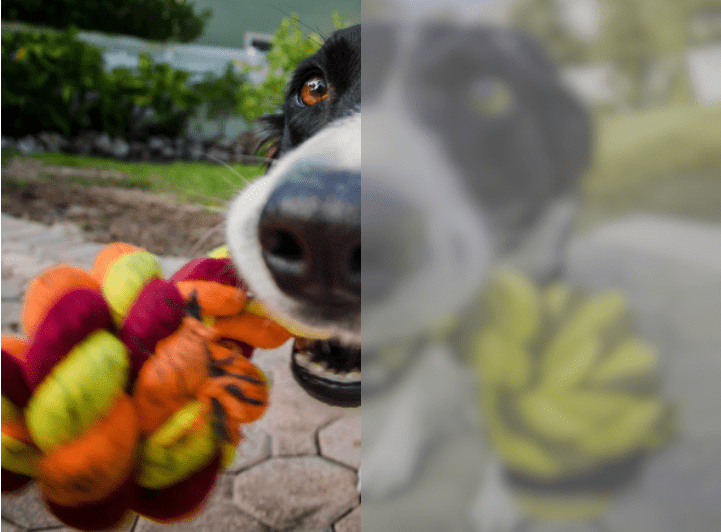
It is because of dichromatic vision that the “tails” do not see red. As for green shades, which dogs allegedly also do not distinguish, the reason here is not the number of cones on the retina, but the fact that in dogs colors do not enter into combinations that can give the same green tone. As a result: in daylight, the surrounding reality for a tailed friend is colored in yellow and blue.

The illustration shows the difference in vision between humans and dogs. Dogs only see in the blue and yellow spectrum. Their vision is blurry, but it has a wider angle.
40 Shades of Grey: Night Vision Features
Positivity and saturation of colors is also not about a person’s friends. Animals perceive all colors available to their receptors in a muted form. That is, the surrounding natural or urban landscape looks to the pet as if on a very cloudy day. The exception is the gray color, in the recognition of which the dog will always be one step ahead of the owner. Actually, thanks to this feature of color perception, the dog is perfectly oriented in twilight and darkness.
Another type of receptor is responsible for the clarity of “night vision” – rods, which are more in dogs than in humans. Therefore, while you are fumbling in the dark along the wall in search of a switch, the pet will calmly inspect the entire space of an unlit room and will never come across objects located in it.
An important role in the quality of the night picture in dogs is played by the tapetum – the reflective membrane of the eye, located behind the retina. In the dark, the tapetum “mirrors” the photons that have passed through the retina, but missed by the rods. As a result, the receptors are given a second opportunity to “catch” the light. If we turn again to the numbers, then the photosensitivity and visual acuity in the dark in a dog are about 5 times higher than in humans. With age, the ability to see perfectly at night in pets deteriorates. Because of this, older individuals often bump into objects and are reluctant to climb steep stairs with the lights off.
Áhugaverð staðreynd: not in all breeds the reflective membrane of the eye is equally developed. The most effective tapetum “works” in dogs of hunting breeds, an order of magnitude worse – in dwarf ones.
In clear weather, when the sun is blinding and makes people take out their sunglasses, the dogs again have the advantage. In the lower part of the retina of animals there is a dark pigment that blocks the penetration of excess light. So while we squint, pets are completely free to view the surrounding landscape without any discomfort.
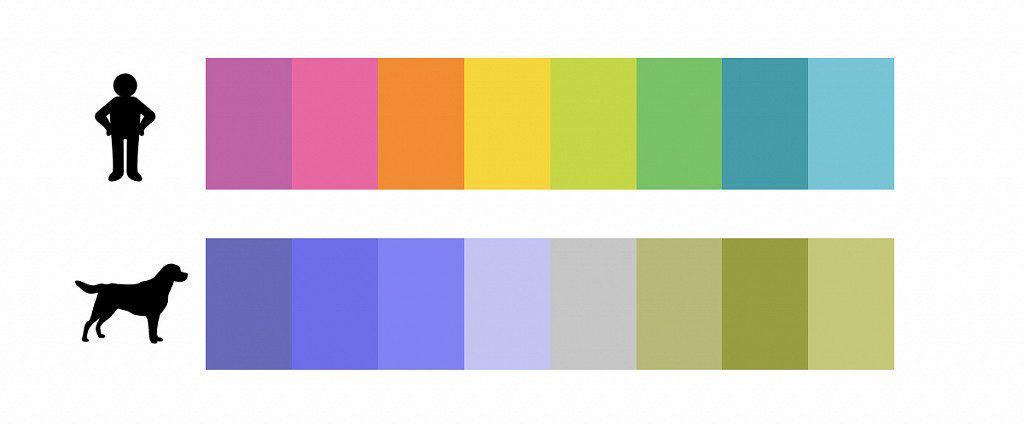

Comparison of the spectrum of human and dog vision
The Blur Effect: How Sharp Are Dogs’ Vision?
Another difference between the dog’s eyes is the absence of a yellow spot, which is responsible for visual acuity. For this reason, a normal healthy animal sees the outlines of surrounding objects more blurry and fuzzy than we do. On average, it is believed that the visual acuity of dogs is 3 times less than that of a person, which is compensated by the breadth of the field of view. In humans, it is about 180 °, in a dog – 240-250 °. And this is an average data. In brachycephals, which have short wide muzzles, peripheral vision is narrower than that of their fellow tribesmen with standard nose sizes. The widest visual coverage is in hunting breeds, the muzzles of whose representatives are narrow, and the angle of divergence of the eyes is much greater than that of the same bulldogs and Pekingese.
Áhugaverð staðreynd: unlike humans, for dogs, vision is not the main source of information about the world around them. The sense of smell and hearing bring an animal an order of magnitude more useful information than the eyes. That is why dogs do not recognize themselves in the mirror, and living objects (people, fellow tribesmen, prey) prefer to identify by smell.
Comparison of human and dog vision angles
Nearsightedness and farsightedness
The fact that a person’s friends see the world as if through a film has given rise to the myth of their myopia. However, studies conducted by employees of the Moscow State Academy of Veterinary Medicine and Biotechnology named after. K. I. Scriabin, show that dogs are rather prone to slight farsightedness (within 0,5 diopters). The majority of adults have about the same indicator.
Thanks to thousands of years of developing predatory and hunting instincts, dogs perfectly capture an object moving at a great distance with their eyes. For example: a person is unlikely to notice a moving hare 700-900 m away, but a dog almost always.
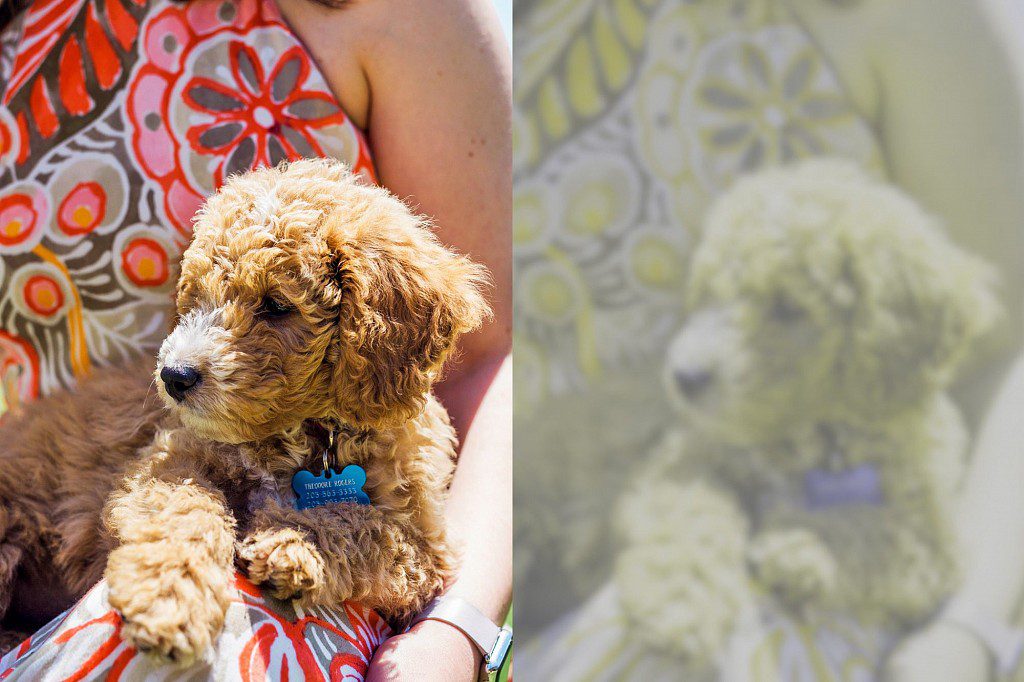
Up close, the sharpness and contrast of a dog’s vision are far inferior to those of a human. For example, even the most tempting treat brought to the face of an animal will look like a strange blurry spot to it. The reason is that the optimal distance for visual “recognition” of a stationary object for dogs is at least 35 cm. Returning to the topic of myopia, it is worth adding that in some breeds it is genetically programmed. For example, Labradors. But to say that all representatives of the canine family suffer from myopia is fundamentally wrong.
Many are also interested in how cats and cats see the world. We also have the answer to this question! You can get acquainted with it in the article: How cats and cats see our world.
Dogs and TV
In order for the image on the screen to be perceived as a continuous visual sequence, and not as a series of pictures replacing each other, a minimum frequency of 20-50 Hz is enough for a person. For dogs, this is not enough, since their organs of vision are able to receive the same impressions only at a frequency of 75 Hz. Therefore, for a long time it was believed that animals were not interested in television, since the old tube devices gave only minimal frame changes up to 60 Hz.
Modern TV receivers are set to a screen refresh rate of 120 Hz. This is more than enough for the perception of the dog. True, as observations show, what is happening on the screen of animals still touches little, and if it attracts attention, then for a very short time. The exception is the categories of videos in which the pet sees and hears its own kind.

With modern TVs, the problem is a thing of the past. All for dogs!
vision problems in dogs
Sad as it may seem, but a person’s friends also lose their sight. The reason for this may be not only the age of the pet. Injuries, untreated inflammatory eye diseases, infections, disruptions in the endocrine system, and even high blood pressure can provoke partial or complete blindness.
How to understand that the dog does not see well
- Moving inside the room, the animal tries to stay against the wall.
- In motion, the pet often bumps into surrounding objects.
- The dog is reluctant to go outside, although he used to be delighted with walks.
- The nervousness and aggressiveness of a four-legged friend in a new environment increases sharply.
- When you wave your hand in front of the muzzle, the dog does not react in any way to your action, and his eyes do not move after the palm.
It is almost impossible to insure your pet against vision loss. But you can always play ahead of the curve, so do not neglect routine examinations in the veterinary office.